2024/5/23
China’s textile and apparel exports perform better than the national trade in goods. Among the main destinations, the exports of the United States, ASEAN and the European Union grew by 3.5%, 6.2% and 0.6% year-on-year, while that to Japan narrowed. The countries along the “Belt and Road” Initiative are still the main booster for textiles and apparel exports, accounting for 55.9% of total exports.
In March, textile and apparel exports did not maintain the momentum seen in the previous two months. The main reason for the 17.4% year-on-year slump is the high comparison base from the same period last year, when there was a backlog of goods exported after the COVID-19 pandemic. Among the four categories of commodities - yarn, fabric, home textiles, and knitted and woven garments - their export prices continued to decline. As for their imports, the yarn and fabric imports increased by 34.8% in March. And cotton imports increased sharply, promising sufficient market supply.
From January to March, the foreign trade of China’s textiles and apparel totaled US$ 71.15 billion, seeing a year-on-year increase of 2.3%. Among them, the exports reached US$ 65.91 billion, up by 1.8% year-on-year; the imports were US$ 5.24 billion, up by 9% year-on-year. In March alone, the foreign trade of textiles and apparel was US$ 22.68 billion, down by 16.1% year-on-year. Thereinto, the exports were US$ 20.82 billion, seeing a decline of 17.4%; and US$ 1.86 billion worth of imports, up by 1.4% year-on-year.
Figure 1: Foreign Trade of China’s Textiles and Apparel from Oct. 2023-Mar. 2024
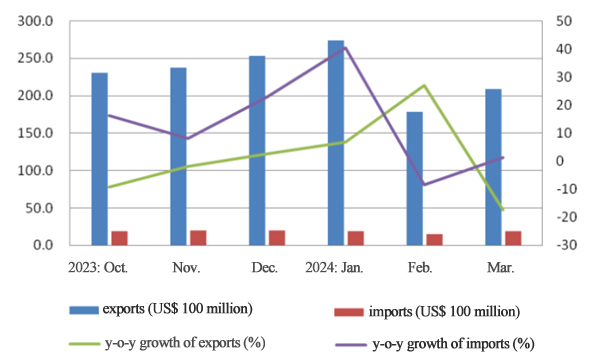
Although the exports in the first quarter of 2024 are lower than those in the same period in 2022, they still outperform the same period in 2021 and 2023. From the perspective of export trends, the current clothing exports are still facing challenges. The uncertainty in the external environment is increasing, and it’s still unclear how foreign demand will recover. Therefore, the industry still needs to accelerate the transformation and upgrading and adjust the global supply chain to cultivate new growth engines for foreign trade.
Looking forward to the second quarter of this year and the near future, China’s textile and apparel exports are expected to face three main challenges: reduced foreign demand, a potential rise in geopolitical conflicts, and trade protectionism. As China’s domestic economy improves, the growing confidence of domestic enterprises and the fast growth of cross-border e-commerce create new opportunities for textile and apparel exports.
Foreign trade of China’s textiles and apparel presents the following characteristics in the first quarter:
1. The overall growth of textile and apparel exports in March narrowed compared with the previous two months.
Affected by various factors like inefficient international shipping, trade disputes, rising tariffs, weak demand, and a high comparison base in March 2023, China experienced a 17.4% year-on-year decline in textile and apparel exports for that month. In the first quarter, textile and apparel exports totaled US$ 65.91 billion, up by 1.8% year-on-year, narrowed by 12 percentage points than the previous two months.
2. Exports to the United States, ASEAN, and the European Union increased, while exports to Japan declined in the first quarter.
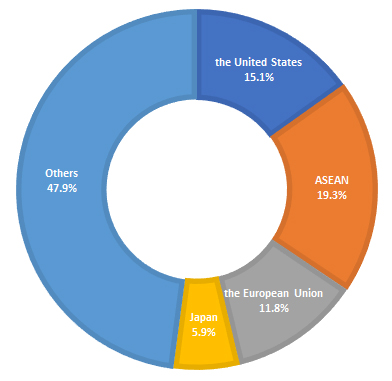
From January to March, China’s textiles and apparel exports to the United States saw a 3.5% year-on-year growth; to ASEAN experienced a year-on-year growth of 6.2%; to the European Union witnessed a year-on-year growth of 0.6%; and exports to Japan fell 9.4% year-on-year. These four significant markets - the United States, ASEAN, the European Union, and Japan - made up 15.1%, 19.3%, 11.8%, and 5.9% of China's exports, totaling 52% of the overall exports. Exports to the 152 countries involved in the "Belt and Road" initiative reached US$ 36.86 billion, showing a 3.1% increase compared to the previous year.
Figure 2: The Share of China’s Textiles and Apparel Exports Destinations in Q1 2024
3. The export performance of China’s main provinces and cities varied in the first quarter.
From January to March, exports increased in Zhejiang Province by 3.4%, in Jiangsu Province by 5.5%, in Shandong Province by 5.1%, and in Fujian Province by 4.5%. However, exports decreased in Guangdong Province by 6.5% and in Shanghai by 3.5%. Xinjiang has experienced export growth of over 30% for six consecutive months, surpassing Shanghai in export value to rank 6th in the country. Fifteen out of 31 provinces, including cities and regions but excluding Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan, experienced export growth. Among them, Guangxi saw a 56% increase, Hubei 42%, Heilongjiang 112%, Shaanxi 57%, and Guizhou 131%. In March, the ranking of the top seven key regions - Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Guangdong, Fujian, and Shanghai - dropped by 26.7%, 15.3%, 34.6%, 11.8%, and 22.1% respectively, influenced by the high base from the same period last year. Exports from Shandong and Xinjiang increased by 20.9% and 16.2% year-on-year.
4. The import value and volume of yarn and apparel have experienced growth.
From January to March, textile and apparel imports totaled US$ 5.24 billion, up by 9% year-on-year. Among them, textile imports reached US$ 2.7 billion, up by 12.3% year-on-year; apparel imports were US$ 2.54 billion, increasing by 5.7% year-on-year. As for commodities, the total import value of yarn increased by 29.9%, imports volume increased by 39.1%; the total import value of fabrics fell by 0.4% year-on-year, and imports volume rose by 4.1%. The import value of knitwear and woven apparel increased by 7.9%, and import volume grew by 2.6% year-on-year.
Source: CHINA TEXTILE LEADER Express



Authority in Charge: China National Textile and Apparel Council (CNTAC)
Sponsor: China Textile Information Center (CTIC)
ISSN 1003-3025 CN11-1714/TS
© 2026 China Textile Leader, all rights reserved.
Powered by SeekRay